Introduction
In an era where speed is synonymous with success, front-end performance optimization is more important than ever. This guide covers essential strategies, from selective rendering to priority-based loading, that can significantly enhance your website's speed, user experience, and search engine ranking.
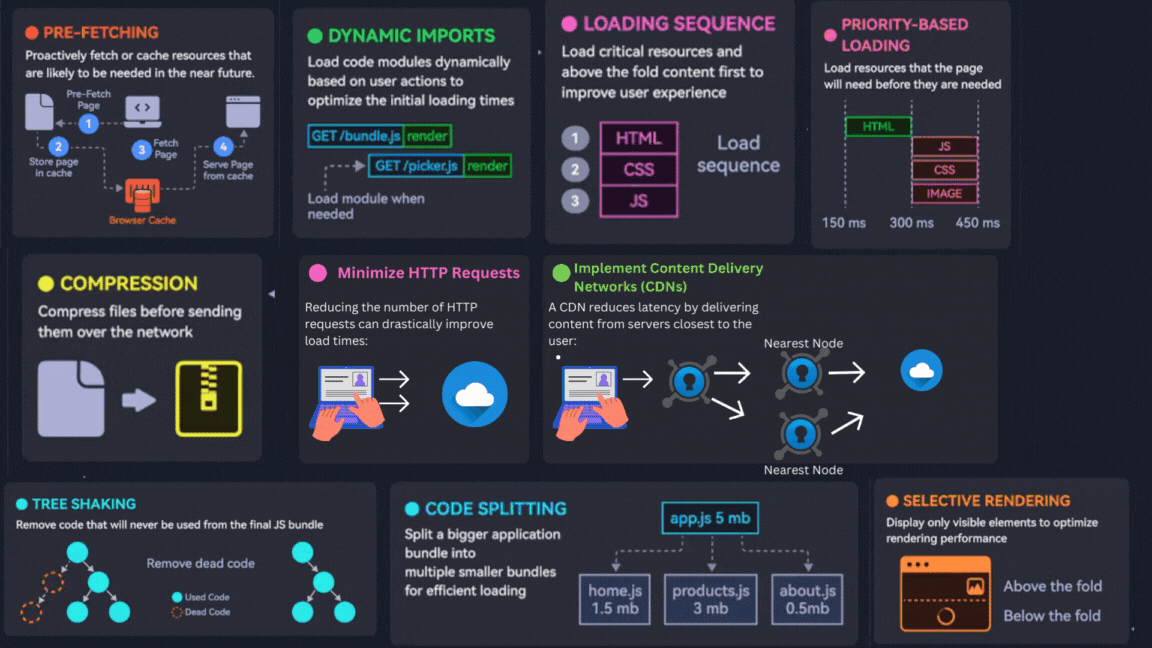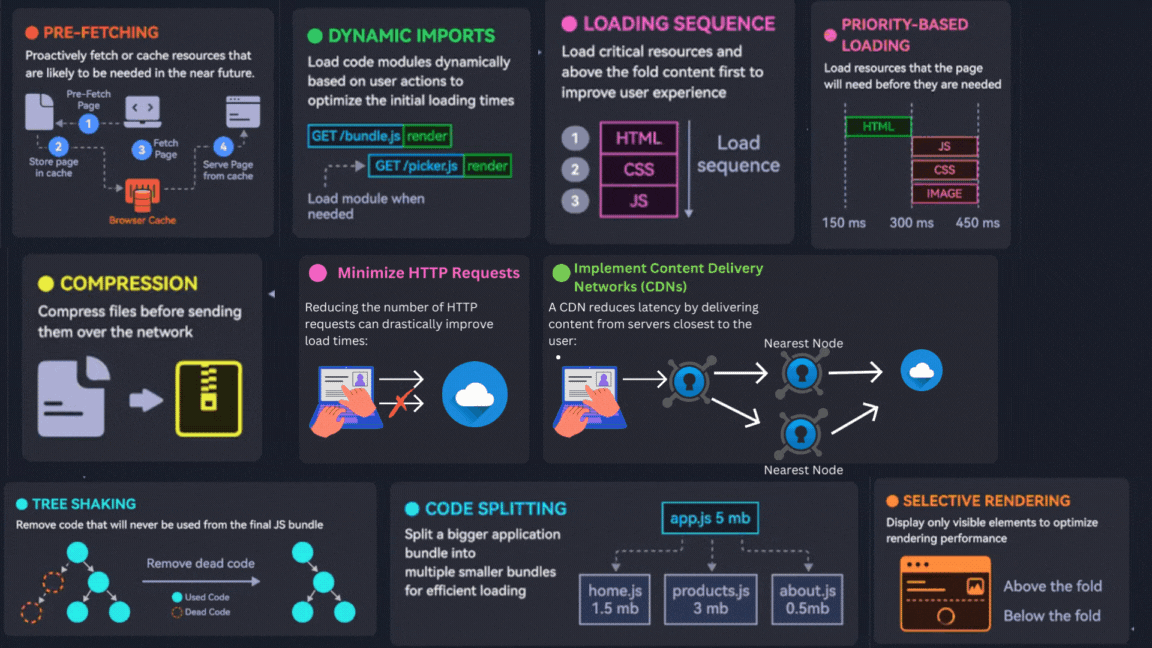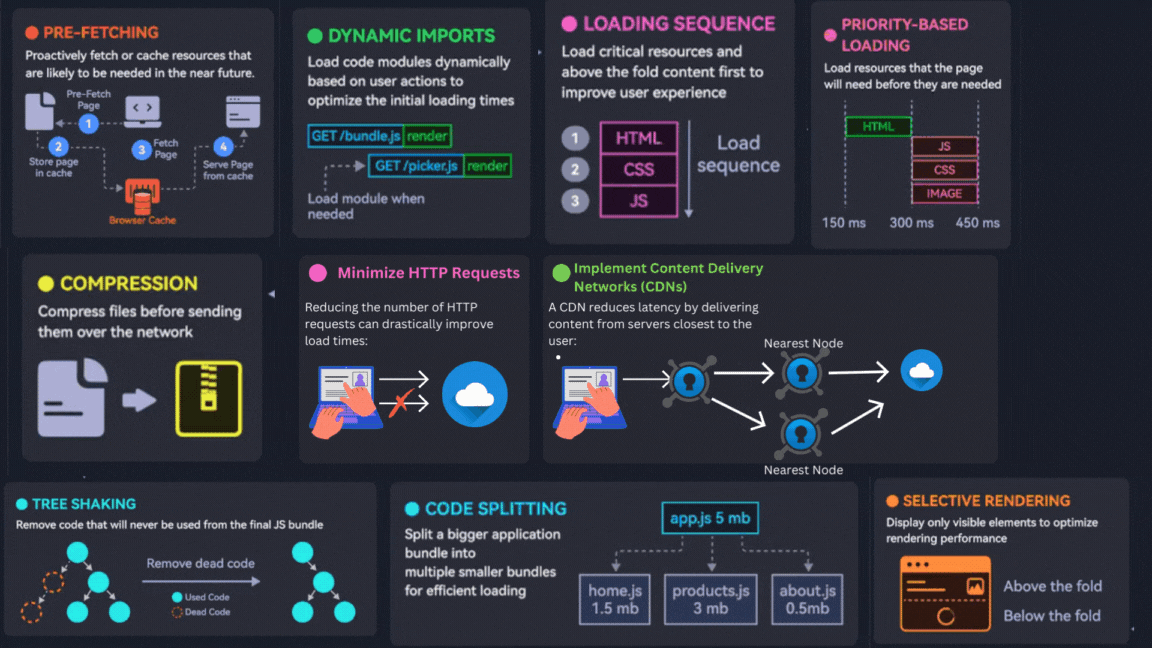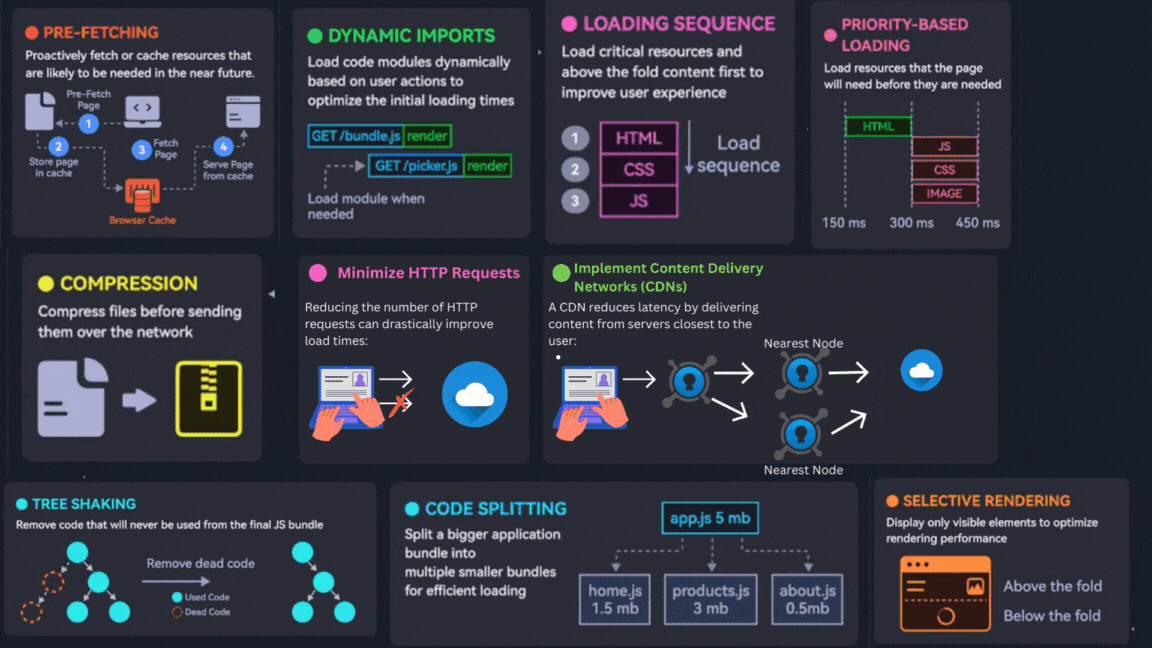
1. Optimize Images
Images often make up a significant portion of a webpage's load time. Optimizing them is crucial:
- Choose the Right Format: Use JPEG for photographs, PNG for images with transparency, and SVG for scalable icons.
- Compress Images: Tools like TinyPNG and ImageOptim can reduce image file sizes without sacrificing quality.
- Lazy Load Images: Utilize lazy loading to only load images when they enter the viewport using the
loading="lazy"attribute or libraries like Lazysizes.
2. Minimize HTTP Requests
Reducing the number of HTTP requests can drastically improve load times:
- Combine Files: Merge multiple CSS and JavaScript files into single files.
- Use CSS Sprites: Combine multiple small images into a single sprite, then use CSS to display specific portions.
- Reduce Redirects: Minimize redirects as they add extra HTTP requests.
3. Selective Rendering
Rendering only the necessary parts of a webpage can enhance performance:
- Server-Side Rendering (SSR): Use SSR for faster initial load times, rendering only what's necessary on the server before sending it to the client.
- Client-Side Rendering (CSR): For subsequent page loads, rely on CSR to reduce server load.
- Component-Based Rendering: Break down the page into smaller components and render them selectively based on user interaction.
4. Prefetching
Prefetching resources can improve perceived performance by loading assets before they are needed:
- DNS Prefetching: Use
<link rel="dns-prefetch" href="//example.com">to resolve domain names early. - Link Prefetching: Use
<link rel="prefetch" href="next-page.html">to load resources that are likely to be needed soon. - Preconnect and Preload: Use
<link rel="preconnect">to establish early connections and<link rel="preload">to fetch critical resources in advance.
5. Optimize Loading Sequence
Properly ordering the loading of resources can prevent render-blocking and speed up page rendering:
- Load Critical CSS First: Inline critical CSS for above-the-fold content and load the rest asynchronously.
- Async and Defer JavaScript: Use the
asyncattribute for scripts that don't depend on others anddeferfor those that do. - Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content: Ensure that the content visible above the fold loads first to improve perceived performance.
6. Compression
Compressing files reduces their size, leading to faster load times:
- Gzip Compression: Enable Gzip on your server to compress HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files.
- Brotli Compression: Consider using Brotli, a newer compression algorithm, for even smaller file sizes.
7. Priority-Based Loading
Assigning different priorities to resources can help load the most important content first:
- Critical Path Optimization: Focus on loading critical resources like CSS and JS for above-the-fold content first.
- Resource Hints: Use
<link rel="preload">for high-priority resources and<link rel="prefetch">for those needed soon after.
8. Code Splitting
Dividing your code into smaller chunks can significantly reduce initial load times:
- Webpack Code Splitting: Use Webpack to split your code into smaller bundles that are loaded as needed.
- Dynamic Imports: Use dynamic
import()in JavaScript to load modules only when they are required. - Route-Based Splitting: For single-page applications, load code based on the route the user is accessing.
9. Leverage Browser Caching
Efficient caching reduces the need to download resources every time a user visits your site:
- Set Cache-Control Headers: Configure your server to send Cache-Control headers with appropriate expiry times.
- Use a CDN: Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to cache resources closer to your users, improving load times.
10. Implement Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN reduces latency by delivering content from servers closest to the user:
- Choose a Reliable CDN: Consider services like Cloudflare, AWS CloudFront, or Akamai.
- Optimize CDN Settings: Set up proper caching rules, SSL settings, and load balancing for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Optimizing front-end performance is an ongoing process that requires attention to detail and a strategic approach. By implementing these advanced techniques—such as selective rendering, prefetching, priority-based loading, and code splitting—you can ensure your website delivers a fast, seamless experience to all users, improving both user satisfaction and SEO performance.